DIY Hydroponic Fish Farming System
Key Takeaways
- Aquaponics combines fish farming with hydroponics for a sustainable food source.
- Creating a small-scale system at home requires planning and understanding of both components.
- Proper maintenance and monitoring are crucial for a successful aquaponics system.
- Various fish and plants can thrive in such systems, depending on your preferences.
- DIY aquaponics can be an enjoyable hobby that contributes to food security.
Introduction
If you’re interested in sustainable living and want to take control of your food sources, creating a DIY hydroponic fish farming system is a fantastic endeavor. This integration of fish farming with hydroponics not only helps in growing vegetables and herbs but also leverages the waste produced by fish as nutrients for plants. Let’s dive into the basics of building your own small-scale aquaponics system.
Understanding the Basics of Aquaponics
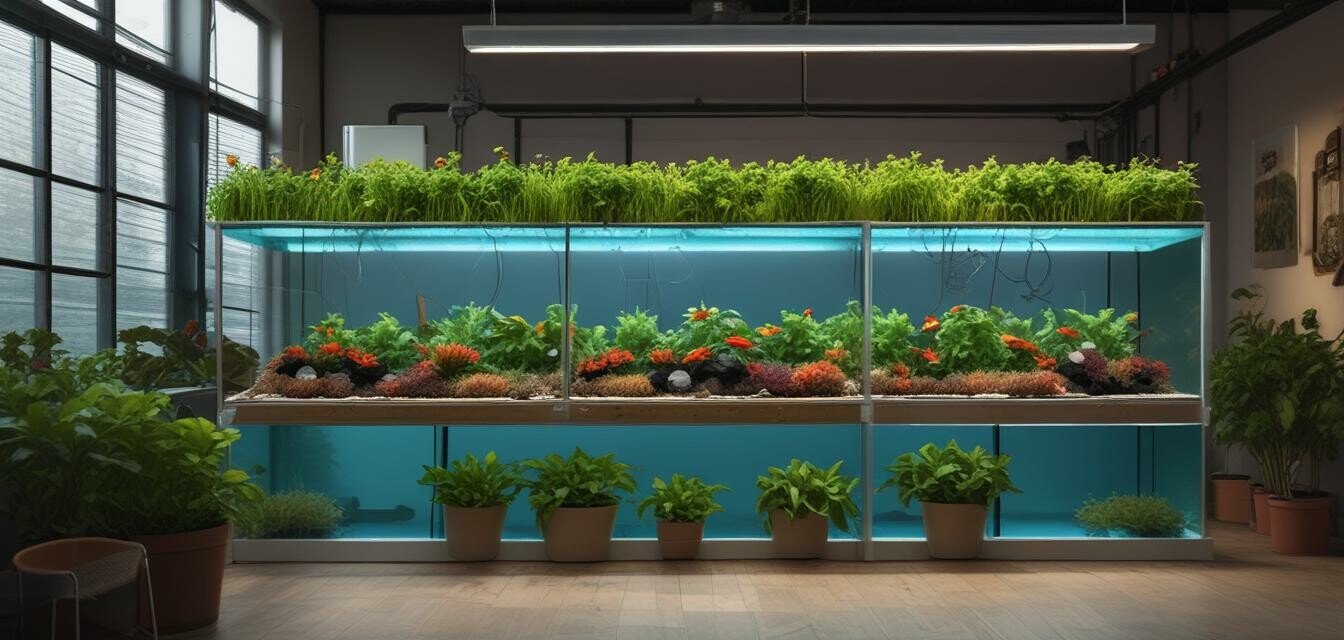
Aquaponics is a symbiotic system that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil). In this system, fish waste provides organic nutrients for the plants, while the plants help filter and clean the water for the fish. This creates a self-sustaining environment that can yield both fish and vegetables.
Components of an Aquaponics System
- Fish Tank: This is where the fish are kept. The size depends on the number and type of fish you plan to raise.
- Grow Bed: A separate area where plants grow, utilizing the nutrient-rich water from the fish tank.
- Pumps: Essential for circulating water between the fish tank and the grow bed.
- Biofilter: A system to convert fish waste into nutrients suitable for plants.
- Air Pump: Keeps the water oxygenated for both fish and plants.
Steps to Build Your DIY Hydroponic Fish Farming System
1. Choose Your Space
Select an appropriate location for your aquaponics system. It should have access to sunlight and a stable temperature. You can operate the system indoors or outdoors, depending on your climate.
2. Select Fish and Plants
Choose fish species that are easy to maintain and fast-growing, like tilapia or goldfish. For plants, herbs such as basil and cilantro or leafy greens like lettuce fit well in an aquaponics system.
3. Build the Fish Tank
Your fish tank can be made of a sturdy plastic or glass container. It should have enough room for the fish to grow comfortably.
4. Create the Grow Bed
The grow bed can be filled with hydroponic media such as clay pellets or rockwool to support the plants. Make sure it can hold enough water while allowing excess to drain back to the fish tank.
5. Install Pump and Filter System
Connect the water pump to the fish tank, leading to the grow bed. Incorporate a biofilter to facilitate the conversion of fish waste into usable nutrients.
6. Set Up Aeration
Use an air pump to provide necessary oxygen to both fish and plant roots. This promotes a healthy aquatic environment.
Maintenance Tips for Your Aquaponics System
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check the water levels and top it off as needed.
- Monitor pH levels; ideally, it should be between 6.8 and 7.0 for most plants.
- Feed fish appropriately and remove any uneaten food to prevent water quality issues.
- Inspect plants for pests and diseases to keep them healthy.
- Perform regular cleanings of the filter and pump to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
A DIY hydroponic fish farming system is not only beneficial for producing food but also acts as a great educational project that allows you to learn about ecosystems. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a sustainable farming method right in your home.
Pros
- Environmentally friendly food production.
- Efficient use of water resources.
- Ability to grow a variety of plants and fish.
- Can be used as an educational tool for families.
- Reduces the carbon footprint related to food transport.
Cons
- Initial setup costs can be high.
- Requires regular maintenance and monitoring.
- Fish health can impact plant growth.
- Learning curve for managing both fish and plants.
- Space requirements can limit setups for small apartments.
Explore More DIY Projects
Continue your journey in hydroponic gardening by exploring our DIY projects section for more innovative ideas and step-by-step guides.